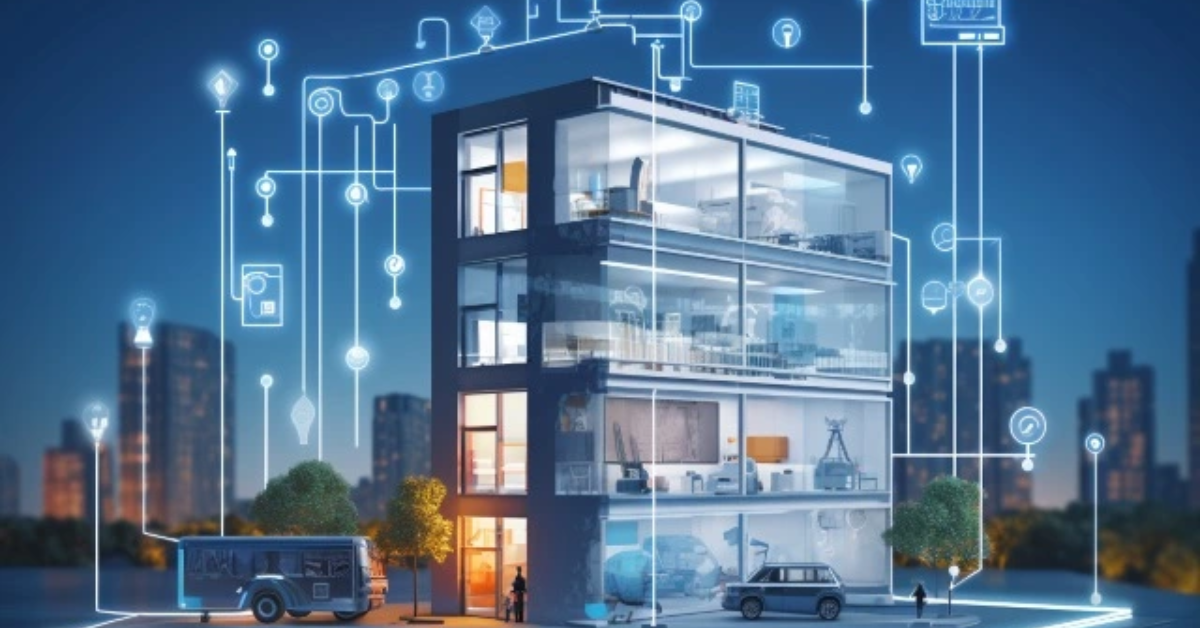
As technology advances, the concept of smart buildings has gained substantial traction. Modern buildings are increasingly outfitted with sophisticated systems designed to enhance efficiency, comfort, and sustainability. Building Automation Systems (BAS), Building Energy Management Systems (BEMS), Building Management Systems (BMS), as well as AI/ML and IoT sensors, play crucial roles in this evolution. These technologies not only streamline building operations but also contribute significantly to energy savings and environmental preservation. This article explores the traditional development of BMS, future directions, and the impact of 75F on the future of BMS.
Building Automation System (BAS)
A Building Automation System (BAS) is a network of hardware and software used to monitor and control a building’s mechanical, electrical, and plumbing systems. Its main goals are to ensure optimal performance, enhance comfort, and reduce energy consumption.
Key Features
1. Centralized Control: BAS provides centralized monitoring and management of all building systems, offering real-time data and enabling rapid responses to issues.
2. Energy Efficiency: By optimizing HVAC and lighting operations, BAS can substantially lower energy use, resulting in cost savings and a smaller environmental footprint.
3. Occupant Comfort: Automated regulation of temperature, lighting, and air quality ensures a comfortable environment for occupants.
4. Integration: BAS can integrate with other systems for a unified approach to building management.
Building Energy Management System (BEMS)
A Building Energy Management System (BEMS) specifically targets energy use within a building. It monitors, analyzes, and manages energy consumption to enhance efficiency and cut costs, often using advanced data analytics to identify trends and recommend improvements.
Key Features
1. Energy Monitoring: BEMS tracks energy usage continuously, providing detailed insights into consumption patterns.
2. Data Analytics: Advanced analytics identify inefficiencies and suggest optimization strategies.
3. Demand Response: BEMS can adjust energy consumption in response to utility signals during peak periods, reducing costs and preventing grid overloads.
4. Sustainability Reporting: BEMS supports sustainability goals by providing data for reporting on energy savings and carbon footprint reductions.
Building Management System (BMS)
A Building Management System (BMS) combines the functionalities of both BAS and BEMS. It integrates various building systems for comprehensive management and control, including HVAC, lighting, security, and fire safety systems.
Key Features
1. Comprehensive Integration: BMS integrates HVAC, lighting, security, fire safety, and energy management systems into a unified platform.
2. User-Friendly Interface: BMS often features intuitive interfaces, allowing building managers to easily monitor and control all systems.
3. Alarm and Event Management: BMS detects and responds to alarms and events, enhancing safety and operational efficiency.
4. Maintenance Management: BMS schedules and tracks maintenance activities, ensuring proper upkeep of systems and reducing unexpected failures.
Benefits of Integrated Building Systems
1. Energy Efficiency and Cost Savings: Integrated systems significantly boost energy efficiency by optimizing various building components, leading to notable cost savings on utilities and operational expenses.
2. Enhanced Comfort and Productivity: Automated control of environmental conditions ensures a comfortable setting for occupants, which can improve productivity and satisfaction in commercial spaces.
3. Improved Safety and Security: Integrating security and fire safety systems within a BMS ensures quick detection and response to emergencies, enhancing overall building safety.
4. Sustainability and Environmental Impact: Reducing energy consumption and optimizing resource use helps lower carbon emissions and supports sustainability initiatives.
Conclusion
Integrating HVAC, lighting, security, and fire safety systems into a single Building Management System (BMS) marks a significant leap in smart building technology. These systems offer a range of benefits, including improved energy efficiency, cost savings, enhanced comfort, and better safety. As the demand for sustainable and intelligent buildings grows, the adoption of these advanced systems will become increasingly widespread, leading to a more efficient and eco-friendly built environment. To future-proof buildings, it’s crucial to upload consolidated data to the cloud and leverage cloud-driven AI/ML technologies to further enhance energy savings and comfort. By using IoT-based sensors, wireless communications, standardized data models, and AI/ML, 75F has significantly improved sensor reliability, installation ease, and energy savings, thus positively impacting customer comfort and operational efficiency.